In a significant leap forward for large language models (LLMs), Google’s researchers have developed a novel technique that dramatically enhances the contextual understanding of these AI systems, enabling them to maintain context indefinitely. This development could revolutionize how AI systems comprehend and interact with complex data streams.
Traditionally, LLMs like GPT-3 or BERT have been constrained by a “context window” — the maximum length of text they can consider at one time, which limits their ability to process information from larger documents or extended conversations. Google’s new approach, outlined in a recent paper and discussed in VentureBeat, introduces a method that allows an LLM to access an unlimited amount of context without overwhelming the model’s memory and processing capabilities.
This technique involves using a dynamic attention mechanism where the model can “remember” and “recall” relevant information from its training data as needed. This is akin to how human memory works, where not all information is actively held in the forefront of our minds but can be recalled as the situation demands. By mimicking this process, Google’s LLM can effectively handle much larger contexts, which is a game-changer for tasks requiring deep contextual understanding, such as summarizing long texts, conducting detailed technical discussions, or managing ongoing dialogues in customer service scenarios.
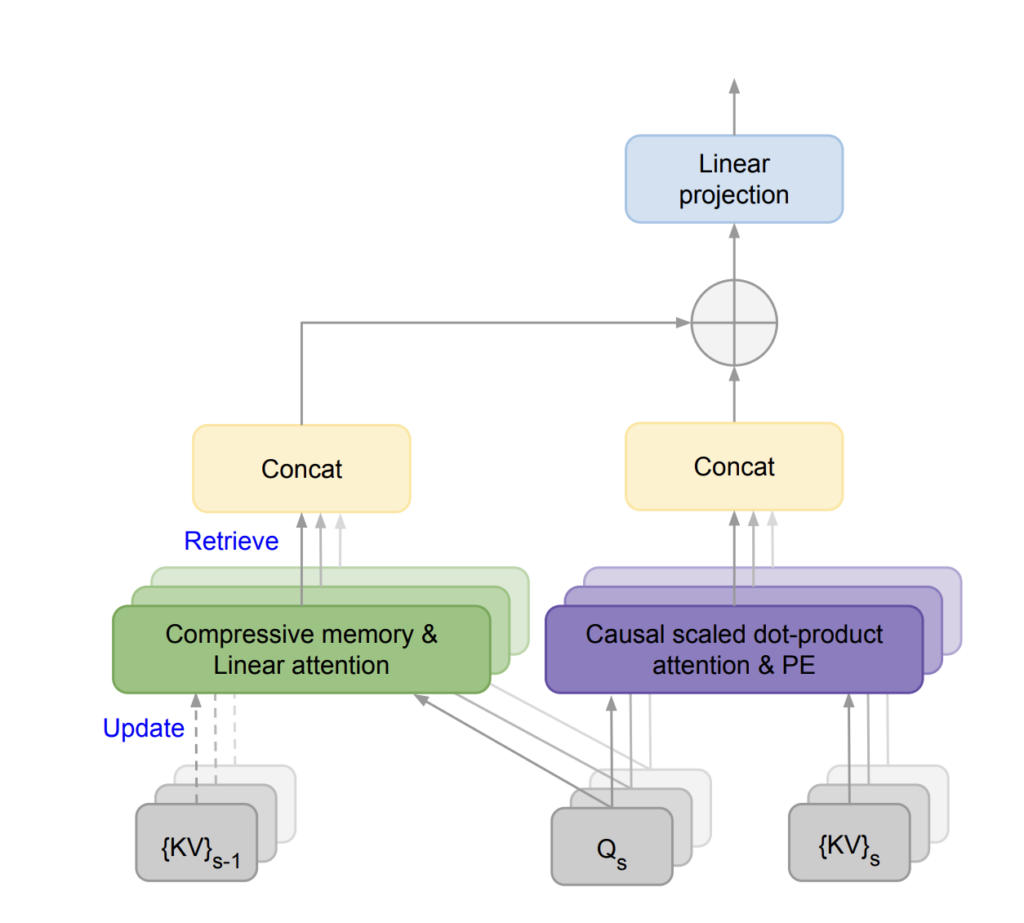
The method leverages a sophisticated blend of machine learning strategies including sparse attention and a memory retrieval system that selectively accesses the most pertinent information from a vast database. This not only expands the model’s effective memory but also ensures computational efficiency, which is critical as AI models grow increasingly complex.
Google’s innovative technique represents a pivotal advancement in the AI field, potentially setting a new standard for how LLMs are developed and deployed. This could lead to more nuanced and intelligent AI systems capable of performing a wider range of tasks with higher accuracy and relevance.
This breakthrough by Google could dramatically expand the potential applications for AI across various industries, from legal and medical professions where large volumes of text must be understood and managed, to customer service and beyond, enhancing the AI’s ability to engage in meaningful and contextually aware interactions.


